This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
통계에 대한 기초적인 이해
가설과 가설검증
- 가설의 종류와 그 종류에 따른 통계분석법
- z-test
- t-test
- ANOVA
- Factorial ANOVA
- correlation
- regression
- multiple regression
- factor analysis
- . . .
- 위를 위해서 꼭 이해해야 할 것들
- Variance
- Standard Deviation
- Standard Error (Standard Deviation of Sample Means)
- Hypothesis Testing
R Cookbook
Chapter 1 Getting Started and Getting Help
Chapter 2 Some Basics
Chapter 3 Navigating the Software
Chapter 4 Input and Output
Chapter 5 Data Structures
Chapter 6 Data Transformations
Chapter 7 Strings and Dates
Chapter 8 Probability
Chapter 9 General Statistics
Chapter 10 Graphics
Chapter 11 Linear Regression and ANOVA
Chapter 12 Useful Tricks
Chapter 13 Beyond Basic Numerics and Statistics
Chapter 14 Time Series Analysis
- Week 01: March 4, 6
- Week 02: March 11, 13
- Week 03: March 18, 20
- Week 04: March 25, 27
- Week 05: April 1, April 3
- Week 06: April 8, 10
- Week 07: April 15, 15
- Week 08: April 22, 24
- Week 09: April 29, May 1
- Week 10: May
6, 8 - Week 11: May 13, 15
- Week 12: May 20, 22
- Week 13: May 27, 28
- Week 14: June 3, June 5
- Week 15: June 10, 12
- Week 16: June 17, 19
Week01
Course Introduction –> syllabus
ideas and concepts
동영상 (R 관련)
- https://youtu.be/J8e5dEH8K_Q 서베이 참여 설명
- https://youtu.be/KYQFY8c2ePI R 과 R studio 인스톨
- https://youtu.be/qCeTcvWBDNY R studio 기초 설명
Introduction to R and others
- Downloading and Installing R
- Starting R
- Entering Commands
- Exiting from R
- Interrupting R
- Viewing the Supplied Documentation
- Getting Help on a Function
- Searching the Supplied Documentation
- Getting Help on a Package
- Searching the Web for Help
- Finding Relevant Functions and Packages
- Searching the Mailing Lists
- Submitting Questions to the Mailing Lists
동영상 (통계관련 샘플링에 대한 설명)
- https://youtu.be/1hJm0O-RY4Q Sampling 과 관련된 아이디어와 용어 설명
기본용어
기술통계 (descriptive statistics)
추론통계 (inferential statistics)
아래의 개념은 샘플링 문서를 먼저 볼것
- 전집 (population)
- 표본 (sample)
- 모수치 (parameter)
- 통계치 (statistics)
- sampling methods
- probability
- non-probability
가설 (hypothesis)
- 차이와 연관 (difference and association)
변인 (variables)
Assignment
etc
What's normal distribution?
?rnorm ?pnorm ?qnorm . . . . rnorm(40,100,10) rnorm(20,0,1) rnorm(20)
rnorm2 <- function(n,mean,sd) { mean+sd*scale(rnorm(n)) }
set.seed(101)
a <- rnorm(1000,100,10)
mean(a)
sd(a)
b <- rnorm2(1000,100,10)
mean(b)
sd(b)
Week02
Concepts and ideas
Sampling
가설
지난 동영상 리캡 및 가설에 대한 소개
가설에 대한 소개 및 설명
가설이 만들어지는 이유
가설의 예
변인의 종류와 변인측정의수준
Some basics
- Introduction
- Printing Something
- Setting Variables
- Listing Variables
- Deleting Variables
- Creating a Vector
- Computing Basic Statistics
- Creating Sequences
- Comparing Vectors
- Selecting Vector Elements
- Performing Vector Arithmetic
- Getting Operator Precedence Right
- Defining a Function
- Typing Less and Accomplishing More
- Avoiding Some Common Mistakes
from the previous lecture (research question and hypothesis)
- Research Questions (or Problems)
- Two ideas guided by theories
- Questions on their relationships
- Conceptualization
-
- Educated guess (via theories)
- Difference
- Association
- Variables (vs. ideas, concepts, and constructs)
-
- Control variable
- Mediating (Intervening) variable
Qs
# normal distribution # see the above [[:normal_distribution]] doc # dnorm = density of normal distribution # pnorm = percentile of normal distribution # qnorm = quantile of normal distribution # rnorm = random sampling of normal distribution dnorm(0,0,1) x <- seq(-5, 5, length=11) span <- c(x) span dnorm(span, 0,1) plot(dnorm(span,0,1)) pnorm(0,0,1) pnorm(1,0,1) pnorm(2) pnorm(3) # volume of the intersection pnorm(1)-pnorm(-1) pnorm(2)-pnorm(-2) pnorm(3)-pnorm(-3) # qnorm qnorm(0.84134478,0,1) qnorm(0.97724988888) qnorm(0.9986501)
> dnorm(0,0,1) [1] 0.3989423 > x <- seq(-5, 5, length=11) > span <- c(x) > span [1] -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 > dnorm(span, 0,1) [1] 1.486720e-06 1.338302e-04 4.431848e-03 5.399097e-02 2.419707e-01 3.989423e-01 2.419707e-01 [8] 5.399097e-02 4.431848e-03 1.338302e-04 1.486720e-06 > plot(dnorm(span,0,1)) > > pnorm(0,0,1) [1] 0.5 > pnorm(1,0,1) [1] 0.8413447 > pnorm(2) [1] 0.9772499 > pnorm(3) [1] 0.9986501 > > # volume of the intersection > pnorm(1)-pnorm(-1) [1] 0.6826895 > pnorm(2)-pnorm(-2) [1] 0.9544997 > pnorm(3)-pnorm(-3) [1] 0.9973002 > > # qnorm > qnorm(0.84134478,0,1) [1] 1 > qnorm(0.97724988888) [1] 2 > qnorm(0.9986501) [1] 3 >
> 0.05/2 [1] 0.025 > qnorm(1-0.025) [1] 1.959964 > qnorm(0.025) [1] -1.959964 > 0.01/2 [1] 0.005 > 1-(0.01/2) [1] 0.995 > qnorm(1-0.005) [1] 2.575829 > qnorm(0.005) [1] -2.575829 > 0.32/2 [1] 0.16 > qnorm(1-0.16) # = 0.84 [1] 0.9944579 > qnorm(0.16) [1] -0.9944579 >
Assignment
Week03
3주차 온라인 강의 동영상은 4주에 걸쳐서 보시기 바랍니다. 즉, 4주 중에 따로 동영상 올리지 않습니다.
- https://youtu.be/JvpOJPCBQkQ : R cookbook: data structure
—–
- https://youtu.be/_ynGzFFmm7U Howell Ch 4. Variance 01: Introduction (DS, error, and SS)
- https://youtu.be/HugtyhU7Im8 Howell Ch. 4. Variance 02: Variance for sample and n-1
- https://youtu.be/RE6DSk1DcJI 왜 분산에는 n-1을 사용하는가? (직관적인 이해)
- https://youtu.be/PrPoOCW3v1s n-1 증명
- https://youtu.be/Ssznnbdj5Lg Degrees of freedom
- https://youtu.be/valhVpf-haY Standard deviation
—–
Howell, Ch. 4 내용 중 Variance와 (분산) Standard deviation은 (표준편차는) 이후 통계 검증방법을 이해하는데 기초가 되는 중요한 내용이니 꼭 숙지하시기 바랍니다.
Concepts and ideas
Navigating software
- Introduction
- Getting and Setting the Working Directory
- Saving Your Workspace
- Viewing Your Command History
- Saving the Result of the Previous Command
- Displaying the Search Path
- Accessing the Functions in a Package
- Accessing Built-in Datasets
- Viewing the List of Installed Packages
- Installing Packages from CRAN
- Setting a Default CRAN Mirror
- Suppressing the Startup Message
- Running a Script
- Running a Batch Script
- Getting and Setting Environment Variables
- Locating the R Home Directory
- Customizing R
+-1 sd = 68% = +-1 sd
+-2 sd = 95% = +-1.96 sd
+-3 sd = 99% (99.7%) = +-3 sd
표준점수 (unit with a standard deviation) = z score
Sampling distribution via random sampling
# +-1SD = 68% # +-2SD = 95% # +-3SD = 99% 라고 했지만 # pnorm(2) = ? pnorm(2) pnorm(2) - pnorm(-2) pnorm(90,70,10) pnorm(90,70,10) - pnorm(50,70,10) pnorm(3) - pnorm(-3) # 95%를 마춰서 생각하려면 qnorm(0.975) # .05의 (1-0.95) 오른쪽 반 qnorm(0.025) # 왼쪽 반 s2.h <- qnorm(.975) # environment panel (r) 체크할 것 s2.l <- qnorm(.025) pnorm(s2.h) - pnorm(s2.l) # 정확히 95% # 1%의 반반씩 생각해보기 s3.h <- qnorm(0.995) s3.l <- qnorm(0.005) pnorm(s3.h) - pnorm(s3.l) # for variance of sample means # see the [[:sampling distribution in r]]
see the sampling distribution in r
Assignment
Week04
동영상 시청
- https://youtu.be/Qaxj6LZ-iL0 : sampling distribution
- https://youtu.be/0RZJbZtzs6s : sampling distribution e.g. in R
- https://youtu.be/AbeIQvJJ5Vw : mean and variance (standard deviation) in sampling distribution (샘플평균들의 집합에서의 평균과 분산 (표준편차))
- https://youtu.be/zFdbt2XoeM4 : CLT (central limit theorem) and standard error 중심극한정리와 표준오차
- https://youtu.be/Udp-4MLAlvc : Testing hypothesis based on CLT principle CLT에 근거를 둔 가설의 검증
Class Activity
Lecture materials for this week
Concepts and ideas
- Introduction
- Entering Data from the Keyboard
- Printing Fewer Digits (or More Digits)
- Redirecting Output to a File
- Listing Files
- Dealing with “Cannot Open File” in Windows
- Reading Fixed-Width Records
- Reading Tabular Data Files
- Reading from CSV Files
- Writing to CSV Files
- Reading Tabular or CSV Data from the Web
- Reading Data from HTML Tables
- Reading Files with a Complex Structure
- Reading from MySQL Databases
- Saving and Transporting Objects
Week05
Concepts and ideas
- Introduction
- Appending Data to a Vector
- Inserting Data into a Vector
- Understanding the Recycling Rule
- Creating a Factor (Categorical Variable)
- Combining Multiple Vectors into One Vector and a Factor
- Creating a List
- Selecting List Elements by Position
- Selecting List Elements by Name
- Building a Name/Value Association List
- Removing an Element from a List
- Flatten a List into a Vector
- Removing NULL Elements from a List
- Removing List Elements Using a Condition
- Initializing a Matrix
- Performing Matrix Operations
- Giving Descriptive Names to the Rows and Columns of a Matrix
- Selecting One Row or Column from a Matrix
- Initializing a Data Frame from Column Data
- Initializing a Data Frame from Row Data
- Appending Rows to a Data Frame
- Preallocating a Data Frame
- Selecting Data Frame Columns by Position
- Selecting Data Frame Columns by Name
- Selecting Rows and Columns More Easily
- Changing the Names of Data Frame Columns
- Editing a Data Frame
- Removing NAs from a Data Frame
- Excluding Columns by Name
- Combining Two Data Frames
- Merging Data Frames by Common Column
- Accessing Data Frame Contents More Easily
- Converting One Atomic Value into Another
- Converting One Structured Data Type into Another
Assignment
#####
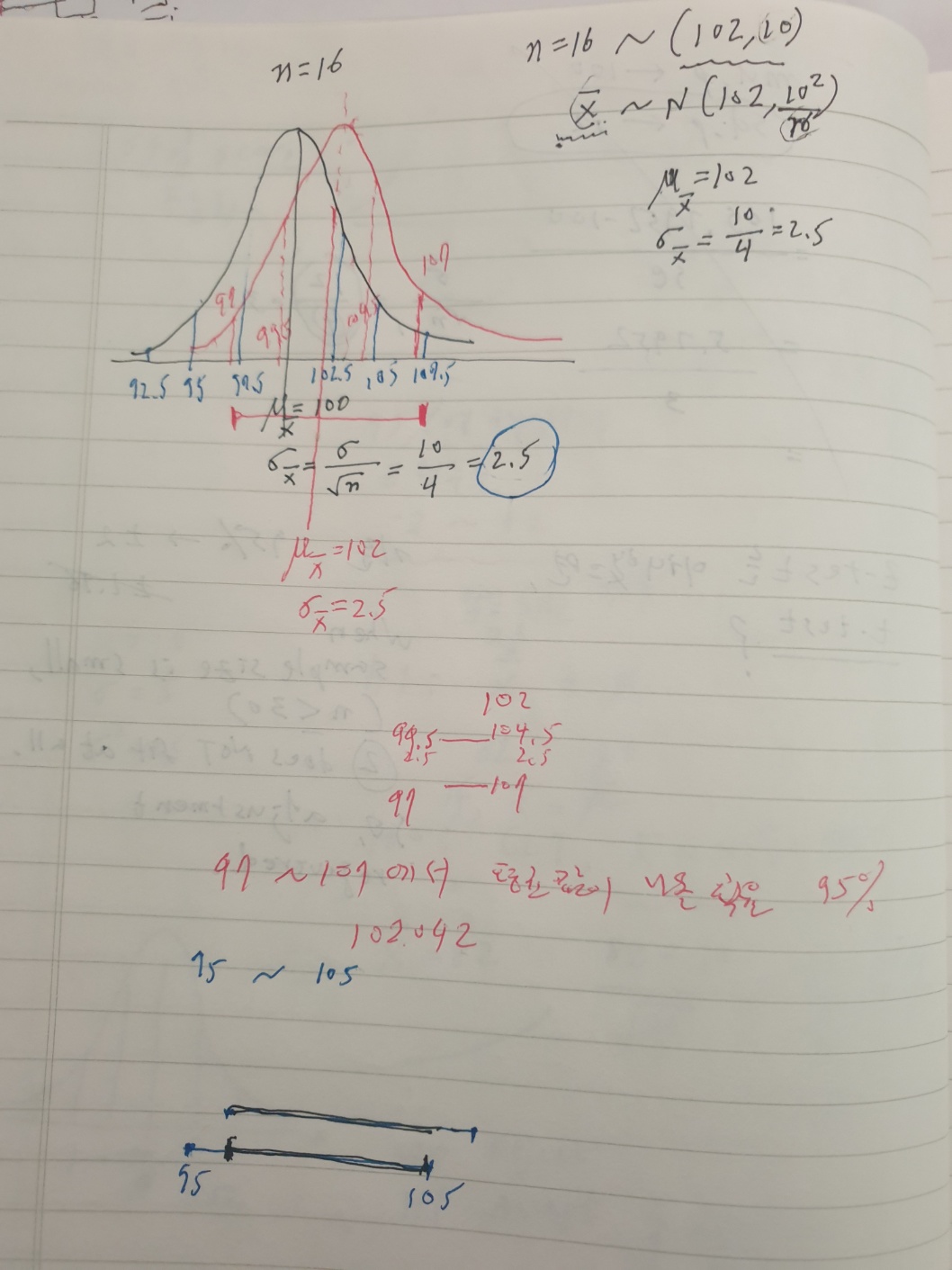
mu.pop <- 100
sd.pop <- 10
set.seed(101)
treated.group <- rnorm(16, 112, 10)
treated.group
m.tg <- mean(treated.group)
m.tg
# H1: m.tg =\ mu.pop (100) ?
# H0: if m.tg =\ mu.pop (100)
# then
# n=16 Xbar ~ N(mu.pop, 25/4)
# 즉 Xbar집합의 분산은 6.25
# 표준편차는 (표준오차, se) 2.5
# 따라서 Xbar 집합의 평균을 중심으로한
# 95% 범위는 pop.mu +- 2*(se)
# 즉, 100중 95는 95 ~ 105 사이에서 샘플의 평균이 나와야 함
# 즉, m.tg는 위의 범위에서 나와야 함. 그러나
# 나머지 5%는 95 밑이나 105 위에서 나올 수도 있음
# 그런데, m.tg = 113.0706
# 이를 근거로 영가설을 부정하고
# 검증하고자 하는 연구가설을 채택함
# 즉, treated group 과 모집단의 평균은 다르다. 혹은
# treated group은 모집단에서 추출될 수 있는 샘플이 아니라
# 다른 모집단에 속한 샘플이다 (95% 확신, 5% 에러마진)
se <- sqrt((sd.pop^2)/16)
qnorm(0.975,mean=100,sd=se)
# [1] 104.8999
qnorm(0.025,mean=100,sd=se)
# [1] 95.10009
# 그렇다면 mu.tg 값이 나올 확률은 몇일까?
pnorm(mu.tg, mean=100, sd=se)
# [1] 0.9999999
sscore <- (m.tg-mu.pop)/se
sscore
# [1] 5.22823
1-pnorm(sscore,0,1)
# [1] 8.557037e-08
a <- 1-pnorm(sscore,0,1)
b <- pnorm(-sscore,0,1)
a
# [1] 8.557037e-08
b
# [1] 8.557037e-08
a+b
# [1] 1.711407e-07
# install.packages("BSDA")
# library(BSDA)
z.test(treated.group, mu=mu.pop, sigma.x=sd.pop)
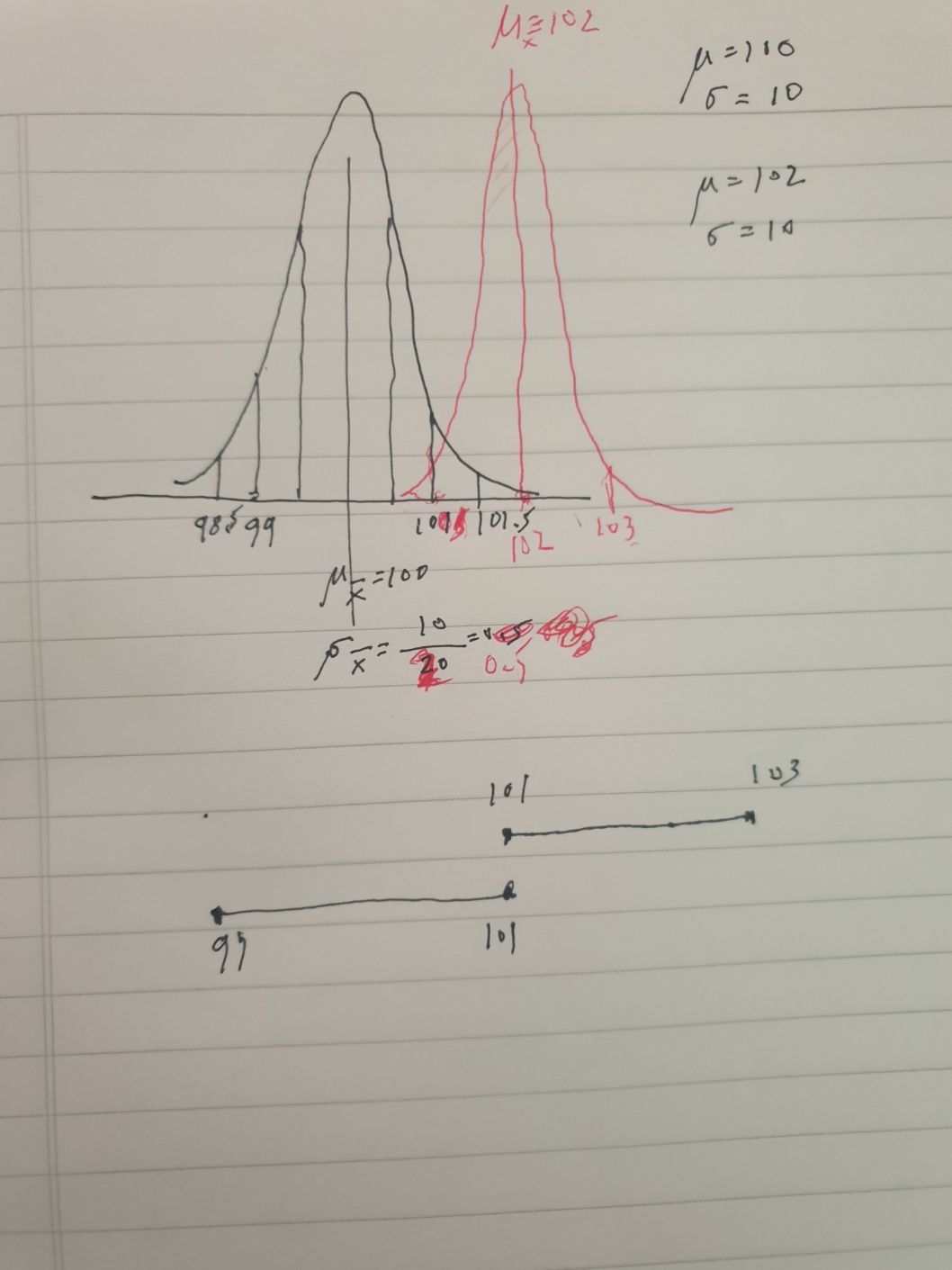
mu.pop <- 100
sd.pop <- 10
set.seed(100)
treated.group.2 <- rnorm(16, 102, 10)
treated.group.2
m.treated.group.2 <- mean(treated.group.2)
m.treated.group.2
# install.packages("BSDA")
# library(BSDA)
z.test(treated.group.2, mu=mu.pop, sigma.x=sd.pop)
set.seed(100)
treated.group.2 <- rnorm(1600, 102, 10)
treated.group.2
m.treated.group.2 <- mean(treated.group.2)
m.treated.group.2
# install.packages("BSDA")
# library(BSDA)
z.test(treated.group.2, mu=mu.pop, sigma.x=sd.pop)
> z.test(treated.group, mu=mu.pop, sigma.x=sd.pop) One-sample z-Test data: treated.group z = 5.2282, p-value = 1.711e-07 alternative hypothesis: true mean is not equal to 100 95 percent confidence interval: 108.1707 117.9705 sample estimates: mean of x 113.0706 > # 위에서 . . . . z 값이 +_2 밖이면 영가설을 부정하고 # 연구가설을 채택하게 된다
# 샘플 숫자가 작을 경우 위의 +-2 점수가 정확하지 # 않기 때문에 보정을 해주게 된다. 이 보정된 값은 # 샘플의 숫자에 따라서 (degrees of freedom) 달 # 라지게 된다
Week06
Concepts and ideas
이번 주 동영상
- https://youtu.be/hX0mbKm6M4s : z-test (z 테스트)
- https://youtu.be/06xTY1cVtb8 : z score (표준점수)
- https://youtu.be/aG8X6EUu7xI : probability in R (R에서의 확률분포함수들)
또한 R에서 데이터를 (테이블 혹은 어레이) 이용하여 function을 적용하는 것에 대해서 잘 익혀두시기 바랍니다. 이는 R cookbook의 아래 내용에 해당이 됩니다 (특히 sapply, tapply, by 등)
- Introduction
- Splitting a Vector into Groups
- Applying a Function to Each List Element
- Applying a Function to Every Row
- Applying a Function to Every Column
- Applying a Function to Groups of Data
- Applying a Function to Groups of Rows
- Applying a Function to Parallel Vectors or Lists
Strings and Dates
# pnorm # qnorm # pt # qt percentage <- .975 df <- 99 t.critical <- qt(percentage, df) # sample size = df + 1 일 때, 95%에 해당하는 점수는? t.critical t.calculated <- 3.6 df <- 8 pt(t.calculated, df)
Announcement
Assignment
Week07
Concepts and ideas
- r 에서 qnorm(proportion) pnorm(z-score) function 이해 필요
- z_score 참조
7주차 동영상
- t-test
- https://youtu.be/Eje8lR8EXPc t-test: Intro
- https://youtu.be/BL9TZbDUVWg t-test: One sample t-test
- https://youtu.be/E7QUCYRcbM0 t-test: Independent samples t-test; repeated measure t-test 일부
- https://youtu.be/CV-DY9xdxtc t-test: Repeated measure t-test 계속
- 관련 문서: t-test
- r 에서, qt(proportion, df), pt(t-score, df) function 이해 필요
- probability 참조
Probability calculation in R ← Probability in R cookbook (텍스트북)
- Introduction
- Counting the Number of Combinations
- Generating Combinations
- Generating Random Numbers
- Generating Reproducible Random Numbers
- Generating a Random Sample
- Generating Random Sequences
- Randomly Permuting a Vector
- Calculating Probabilities for Discrete Distributions
- Calculating Probabilities for Continuous Distributions
- Converting Probabilities to Quantiles
- Plotting a Density Function
Assignment
- 가설 만들어 보기
- how to write hypothesis at behavioral science writing.
- One sample hypothesis Hypothesis at www.socialresearchmethods.net
8주차 퀴즈
8주차 정기시험기간 중에 2차 퀴즈
- 시간
- 09:00 ~ (A, B교시)
- 범위
- 처음부터 One-way ANOVA test with post hoc test 까지 (R square에 대한 설명포함)
- 제 9주차 내용이지만 수업시간에 다룬 것만 시험에 나옵니다.
- 동영상은 7주차까지 보셔야 합니다
Week08
시험기간
Week09
Concepts and ideas
영상 ANOVA
- https://youtu.be/bNK5iIjAoHI : Intro to ANOVA (F-test)
- https://youtu.be/L9ns0vuvWJ8 : principles of ANOVA
- https://youtu.be/xOixsz4Qkz0 : ANOVA, calculation based on the priciple
- https://youtu.be/kyVXFS3jts4 : post-hoc test / t-test vs. ANOVA
위키페이지 참조
- Introduction
- Summarizing Your Data
- Calculating Relative Frequencies
- Tabulating Factors and Creating Contingency Tables
- Testing Categorical Variables for Independence
- Calculating Quantiles (and Quartiles) of a Dataset
- Inverting a Quantile
- Converting Data to Z-Scores
- Testing the Mean of a Sample (t Test)
- Forming a Confidence Interval for a Mean
- Forming a Confidence Interval for a Median
- Testing a Sample Proportion
- Forming a Confidence Interval for a Proportion
- Testing for Normality
- Testing for Runs
- Comparing the Means of Two Samples
- Comparing the Locations of Two Samples Nonparametrically
- Testing a Correlation for Significance
- Testing Groups for Equal Proportions
- Performing Pairwise Comparisons Between Group Means
- Testing Two Samples for the Same Distribution
vene . . . go or come
intervene
- intervenient
convene
- convention
- convent
- convenient
contravene
prevent
advent
circumvent
Assignment
Week10
Concepts and ideas
10주차 동영상입니다.
- https://youtu.be/IpuyWhk1R9g : Factorial ANOVA
- https://youtu.be/UuJhej1eJJI : Factorial ANOVA by hand
- https://youtu.be/rl6zs1lK0BE : Factorial ANOVA egs.
see w10.lecture.note
Assignment
Week11
Concepts and ideas
동영상 (총 5 개)
- https://youtu.be/vwxdhllHM-8 : Repeated Measures ANOVA, Intro
- https://youtu.be/L_jzB650Llo : Repeated Measures ANOVA in R
—-
- https://youtu.be/Cj7mxGBrIU8 : Correlations 01
- https://youtu.be/oYKFeuAn140 : Correlations 02
- https://youtu.be/aHdb4j3ybX8 : Spearman (Rank ordered) Correlation
regression
multiple regression
using dummy variables
getting started
basics
navigating in r
input output in r
data structures
data transformations
- Introduction
- Creating a Scatter Plot
- Adding a Title and Labels
- Adding a Grid
- Creating a Scatter Plot of Multiple Groups
- Adding a Legend
- Plotting the Regression Line of a Scatter Plot
- Plotting All Variables Against All Other Variables
- Creating One Scatter Plot for Each Factor Level
- Creating a Bar Chart
- Adding Confidence Intervals to a Bar Chart
- Coloring a Bar Chart
- Plotting a Line from x and y Points
- Changing the Type, Width, or Color of a Line
- Plotting Multiple Datasets
- Adding Vertical or Horizontal Lines
- Creating a Box Plot
- Creating One Box Plot for Each Factor Level
- Creating a Histogram
- Adding a Density Estimate to a Histogram
- Creating a Discrete Histogram
- Creating a Normal Quantile-Quantile (Q-Q) Plot
- Creating Other Quantile-Quantile Plots
- Plotting a Variable in Multiple Colors
- Graphing a Function
- Pausing Between Plots
- Displaying Several Figures on One Page
- Opening Additional Graphics Windows
- Writing Your Plot to a File
- Changing Graphical Parameters
Assignment
과제명: ms23.w11.ga.covariance.exercise
제출파일명: ms23.w11.ga.covariance.exercise.group##.odc (docx)
과제내용:
아래 데이터를 다운로드 받아서 두 변인 간의 상관관계계수를 구하시오.
income.happiness.csv
income.happiness.cat.csv
데이터는 수입과 행복을 측정한 것입니다. 실제 데이터를 살펴보고 R로 읽어 온 후에 R을 이용하여 아래를 구하시오. R에서의 명령어와 아웃풋을 카피/패이스트 하여 제출하시오 (fixed-font를 사용하여).
- 각 변인의 deviation score 값을 구하여 ds.inc 와 ds.hap 에 저장하시오.
- 두 변인의 SP값을 (Sum of Product) 구하여 sp.dat 에 저장하시오.
- 두 변인의 df값을 구하여 df.dat 에 저장하시오.
- 두 변인간 covariance값을 r의 cov 명령어를 이용하여 구하여 cov.dat값에 저장하시오.
- sp.dat / df.dat 값을 구하여 cov.cal 값에 저장하시오.
- cov.cal 과 cov.dat 값이 같은지 비교하시오. (힌트:
==연산자를 이용하여 확인하시오) - 각 변인의 standard deviation 값을 구하여 sd.inc, sd.hap에 저장하시오
- 우리가 배운 correlation값을 구하는 공식에 따라서 r 값을 구해서 r.cal 에 저장하시오.
- R의 cor 명령어를 이용하여 correlation coefficient값을 구하여 r.dat 에 저장하시오.
- r.cal 과 r.dat 을 비교하시오.
Week12
May 22 (월), 24 (수)
Announcement
Concepts and ideas
regression lecture note for r
동영상 Regression
- https://youtu.be/68gho4ubOjs : Regression 1. Intro
- https://youtu.be/qXSRgSh1rw0 : Regression 2. e.g. 1
- https://youtu.be/I8wt2W7-Iio : Regression 3. e.g. 2
Assignment
Week13
영상
- https://youtu.be/LOEinkXaskA : Multiple Regression 01 Intro.
- https://youtu.be/v6LswXPvEWY : Multiple Regression 03 Interpreting ivs
- https://youtu.be/tc6wb7fBmiY : Week13 Multiple Regression 02 Dummy variables
multiple regression lecture note for r
multiple regression
-
- option reading using dummy variables with spss
statistical regression← 다루지 않습니다
Concepts and ideas
Assignment
Week14
June 5(월), 7(수)
13주차 참조
Concepts and ideas
Assignment
Week15
June 12, 14
13주차 참조
Assignment
Week16
June 19, 21 (퀴즈일자에만 퀴즈를 보고 수업은 없음)
Final-term
- 마지막 퀴즈
- 범위는 다음과 같습니다.
- Statistics
- R 관련 문제는 아웃풋을 이해하는지에 치중을 하시면 됩니다. 실제 명령어 사용 등에 대한 문제는 나오지 않습니다.