This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
통계에 대한 기초적인 이해
가설과 가설검증
- 가설의 종류와 그 종류에 따른 통계분석법
- z-test
- t-test
- ANOVA
- Factorial ANOVA
- correlation
- regression
- multiple regression
- factor analysis
- . . .
- 위를 위해서 꼭 이해해야 할 것들
- Variance
- Standard Deviation
- Standard Error (Standard Deviation of Sample Means)
- Hypothesis Testing
R Cookbook
Chapter 1 Getting Started and Getting Help
Chapter 2 Some Basics
Chapter 3 Navigating the Software
Chapter 4 Input and Output
Chapter 5 Data Structures
Chapter 6 Data Transformations
Chapter 7 Strings and Dates
Chapter 8 Probability
Chapter 9 General Statistics
Chapter 10 Graphics
Chapter 11 Linear Regression and ANOVA
Chapter 12 Useful Tricks
Chapter 13 Beyond Basic Numerics and Statistics
Chapter 14 Time Series Analysis
- Week 01: March 4, 6
- Week 02: March 11, 13
- Week 03: March 18, 20
- Week 04: March 25, 27
- Week 05: April 1, April 3
- Week 06: April 8, 10
- Week 07: April 15, 15
- Week 08: April 22, 24
- Week 09: April 29, May 1
- Week 10: May
6, 8 - Week 11: May 13, 15
- Week 12: May 20, 22
- Week 13: May 27, 28
- Week 14: June 3, June 5
- Week 15: June 10, 12
- Week 16: June 17, 19
Week01
Course Introduction –> syllabus
ideas and concepts
동영상 (R 관련)
- https://youtu.be/J8e5dEH8K_Q 서베이 참여 설명
- https://youtu.be/KYQFY8c2ePI R 과 R studio 인스톨
- https://youtu.be/qCeTcvWBDNY R studio 기초 설명
Introduction to R and others
- Downloading and Installing R
- Starting R
- Entering Commands
- Exiting from R
- Interrupting R
- Viewing the Supplied Documentation
- Getting Help on a Function
- Searching the Supplied Documentation
- Getting Help on a Package
- Searching the Web for Help
- Finding Relevant Functions and Packages
- Searching the Mailing Lists
- Submitting Questions to the Mailing Lists
동영상 (통계관련 샘플링에 대한 설명)
- https://youtu.be/1hJm0O-RY4Q Sampling 과 관련된 아이디어와 용어 설명
기본용어
기술통계 (descriptive statistics)
추론통계 (inferential statistics)
아래의 개념은 샘플링 문서를 먼저 볼것
- 전집 (population)
- 표본 (sample)
- 모수치 (parameter)
- 통계치 (statistics)
- sampling methods
- probability
- non-probability
가설 (hypothesis)
- 차이와 연관 (difference and association)
변인 (variables)
Assignment
etc
What's normal distribution?
?rnorm ?pnorm ?qnorm . . . . rnorm(40,100,10) rnorm(20,0,1) rnorm(20)
rnorm2 <- function(n,mean,sd) { mean+sd*scale(rnorm(n)) }
set.seed(101)
a <- rnorm(1000,100,10)
mean(a)
sd(a)
b <- rnorm2(1000,100,10)
mean(b)
sd(b)
Week02
Concepts and ideas
Sampling
가설
지난 동영상 리캡 및 가설에 대한 소개
가설에 대한 소개 및 설명
가설이 만들어지는 이유
가설의 예
변인의 종류와 변인측정의수준
Some basics
- Introduction
- Printing Something
- Setting Variables
- Listing Variables
- Deleting Variables
- Creating a Vector
- Computing Basic Statistics
- Creating Sequences
- Comparing Vectors
- Selecting Vector Elements
- Performing Vector Arithmetic
- Getting Operator Precedence Right
- Defining a Function
- Typing Less and Accomplishing More
- Avoiding Some Common Mistakes
from the previous lecture (research question and hypothesis)
- Research Questions (or Problems)
- Two ideas guided by theories
- Questions on their relationships
- Conceptualization
-
- Educated guess (via theories)
- Difference
- Association
- Variables (vs. ideas, concepts, and constructs)
-
- Control variable
- Mediating (Intervening) variable
Qs
# normal distribution # see the above [[:normal_distribution]] doc # dnorm = density of normal distribution # pnorm = percentile of normal distribution # qnorm = quantile of normal distribution # rnorm = random sampling of normal distribution dnorm(0,0,1) x <- seq(-5, 5, length=11) span <- c(x) span dnorm(span, 0,1) plot(dnorm(span,0,1)) pnorm(0,0,1) pnorm(1,0,1) pnorm(2) pnorm(3) # volume of the intersection pnorm(1)-pnorm(-1) pnorm(2)-pnorm(-2) pnorm(3)-pnorm(-3) # qnorm qnorm(0.84134478,0,1) qnorm(0.97724988888) qnorm(0.9986501)
> dnorm(0,0,1) [1] 0.3989423 > x <- seq(-5, 5, length=11) > span <- c(x) > span [1] -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 > dnorm(span, 0,1) [1] 1.486720e-06 1.338302e-04 4.431848e-03 5.399097e-02 2.419707e-01 3.989423e-01 2.419707e-01 [8] 5.399097e-02 4.431848e-03 1.338302e-04 1.486720e-06 > plot(dnorm(span,0,1)) > > pnorm(0,0,1) [1] 0.5 > pnorm(1,0,1) [1] 0.8413447 > pnorm(2) [1] 0.9772499 > pnorm(3) [1] 0.9986501 > > # volume of the intersection > pnorm(1)-pnorm(-1) [1] 0.6826895 > pnorm(2)-pnorm(-2) [1] 0.9544997 > pnorm(3)-pnorm(-3) [1] 0.9973002 > > # qnorm > qnorm(0.84134478,0,1) [1] 1 > qnorm(0.97724988888) [1] 2 > qnorm(0.9986501) [1] 3 >
> 0.05/2 [1] 0.025 > qnorm(1-0.025) [1] 1.959964 > qnorm(0.025) [1] -1.959964 > 0.01/2 [1] 0.005 > 1-(0.01/2) [1] 0.995 > qnorm(1-0.005) [1] 2.575829 > qnorm(0.005) [1] -2.575829 > 0.32/2 [1] 0.16 > qnorm(1-0.16) # = 0.84 [1] 0.9944579 > qnorm(0.16) [1] -0.9944579 >
Assignment
Week03
3주차 온라인 강의 동영상은 4주에 걸쳐서 보시기 바랍니다. 즉, 4주 중에 따로 동영상 올리지 않습니다.
- https://youtu.be/JvpOJPCBQkQ : R cookbook: data structure
—–
- https://youtu.be/_ynGzFFmm7U Howell Ch 4. Variance 01: Introduction (DS, error, and SS)
- https://youtu.be/HugtyhU7Im8 Howell Ch. 4. Variance 02: Variance for sample and n-1
- https://youtu.be/RE6DSk1DcJI 왜 분산에는 n-1을 사용하는가? (직관적인 이해)
- https://youtu.be/PrPoOCW3v1s n-1 증명
- https://youtu.be/Ssznnbdj5Lg Degrees of freedom
- https://youtu.be/valhVpf-haY Standard deviation
—–
Howell, Ch. 4 내용 중 Variance와 (분산) Standard deviation은 (표준편차는) 이후 통계 검증방법을 이해하는데 기초가 되는 중요한 내용이니 꼭 숙지하시기 바랍니다.
Concepts and ideas
Navigating software
- Introduction
- Getting and Setting the Working Directory
- Saving Your Workspace
- Viewing Your Command History
- Saving the Result of the Previous Command
- Displaying the Search Path
- Accessing the Functions in a Package
- Accessing Built-in Datasets
- Viewing the List of Installed Packages
- Installing Packages from CRAN
- Setting a Default CRAN Mirror
- Suppressing the Startup Message
- Running a Script
- Running a Batch Script
- Getting and Setting Environment Variables
- Locating the R Home Directory
- Customizing R
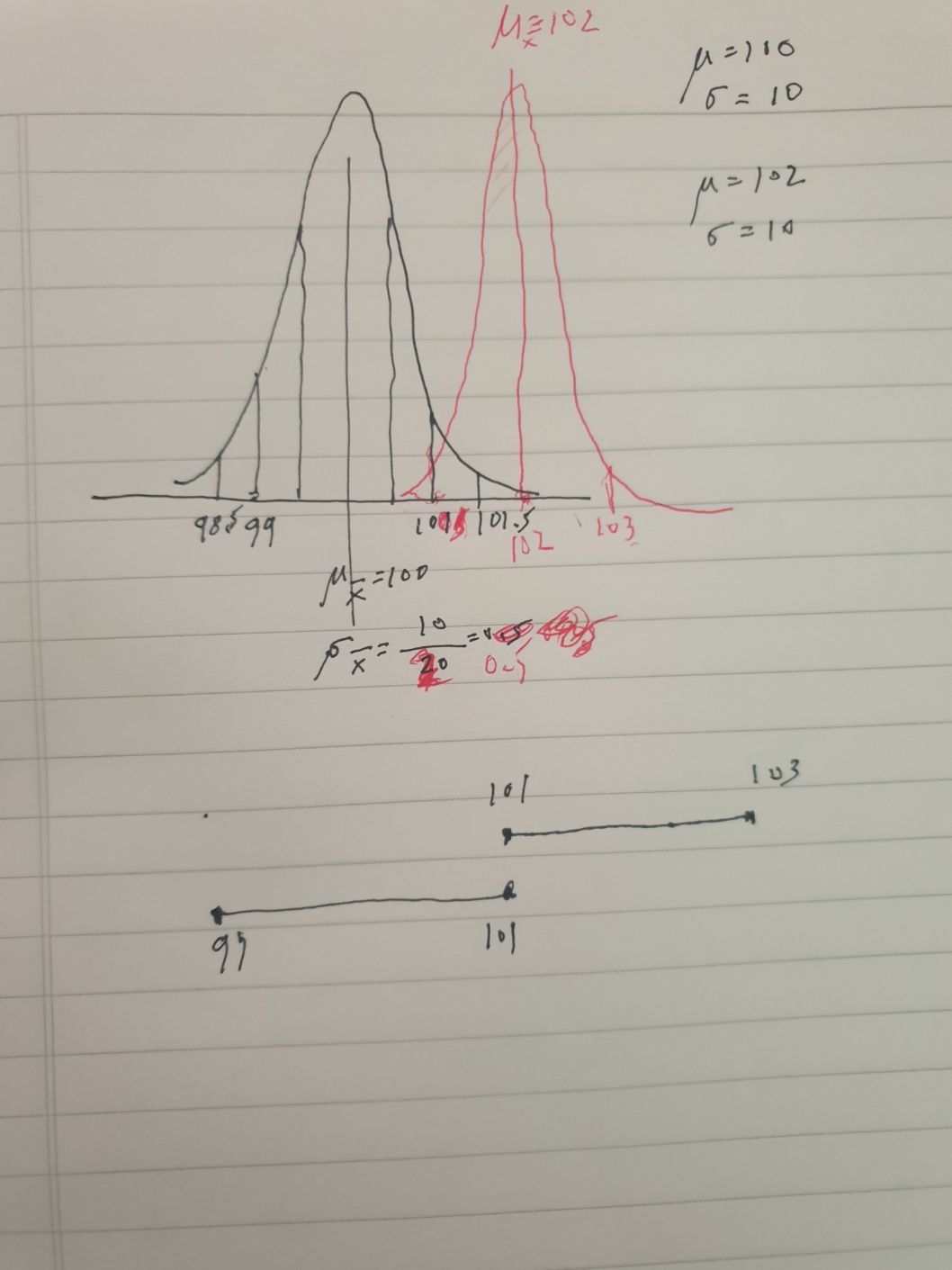
+-1 sd = 68% = +-1 sd
+-2 sd = 95% = +-1.96 sd
+-3 sd = 99% (99.7%) = +-3 sd
표준점수 (unit with a standard deviation) = z score
Sampling distribution via random sampling
# +-1SD = 68% # +-2SD = 95% # +-3SD = 99% 라고 했지만 # pnorm(2) = ? pnorm(2) pnorm(2) - pnorm(-2) pnorm(90,70,10) pnorm(90,70,10) - pnorm(50,70,10) pnorm(3) - pnorm(-3) # 95%를 마춰서 생각하려면 qnorm(0.975) # .05의 (1-0.95) 오른쪽 반 qnorm(0.025) # 왼쪽 반 s2.h <- qnorm(.975) # environment panel (r) 체크할 것 s2.l <- qnorm(.025) pnorm(s2.h) - pnorm(s2.l) # 정확히 95% # 1%의 반반씩 생각해보기 s3.h <- qnorm(0.995) s3.l <- qnorm(0.005) pnorm(s3.h) - pnorm(s3.l) # for variance of sample means # see the [[:sampling distribution in r]]
see the sampling distribution in r
Assignment
Week04
동영상 시청
- https://youtu.be/Qaxj6LZ-iL0 : sampling distribution
- https://youtu.be/0RZJbZtzs6s : sampling distribution e.g. in R
- https://youtu.be/AbeIQvJJ5Vw : mean and variance (standard deviation) in sampling distribution (샘플평균들의 집합에서의 평균과 분산 (표준편차))
- https://youtu.be/zFdbt2XoeM4 : CLT (central limit theorem) and standard error 중심극한정리와 표준오차
- https://youtu.be/Udp-4MLAlvc : Testing hypothesis based on CLT principle CLT에 근거를 둔 가설의 검증
Class Activity
Lecture materials for this week
Concepts and ideas
- Introduction
- Entering Data from the Keyboard
- Printing Fewer Digits (or More Digits)
- Redirecting Output to a File
- Listing Files
- Dealing with “Cannot Open File” in Windows
- Reading Fixed-Width Records
- Reading Tabular Data Files
- Reading from CSV Files
- Writing to CSV Files
- Reading Tabular or CSV Data from the Web
- Reading Data from HTML Tables
- Reading Files with a Complex Structure
- Reading from MySQL Databases
- Saving and Transporting Objects
Week05
Concepts and ideas
- Introduction
- Appending Data to a Vector
- Inserting Data into a Vector
- Understanding the Recycling Rule
- Creating a Factor (Categorical Variable)
- Combining Multiple Vectors into One Vector and a Factor
- Creating a List
- Selecting List Elements by Position
- Selecting List Elements by Name
- Building a Name/Value Association List
- Removing an Element from a List
- Flatten a List into a Vector
- Removing NULL Elements from a List
- Removing List Elements Using a Condition
- Initializing a Matrix
- Performing Matrix Operations
- Giving Descriptive Names to the Rows and Columns of a Matrix
- Selecting One Row or Column from a Matrix
- Initializing a Data Frame from Column Data
- Initializing a Data Frame from Row Data
- Appending Rows to a Data Frame
- Preallocating a Data Frame
- Selecting Data Frame Columns by Position
- Selecting Data Frame Columns by Name
- Selecting Rows and Columns More Easily
- Changing the Names of Data Frame Columns
- Editing a Data Frame
- Removing NAs from a Data Frame
- Excluding Columns by Name
- Combining Two Data Frames
- Merging Data Frames by Common Column
- Accessing Data Frame Contents More Easily
- Converting One Atomic Value into Another
- Converting One Structured Data Type into Another
Assignment
#####
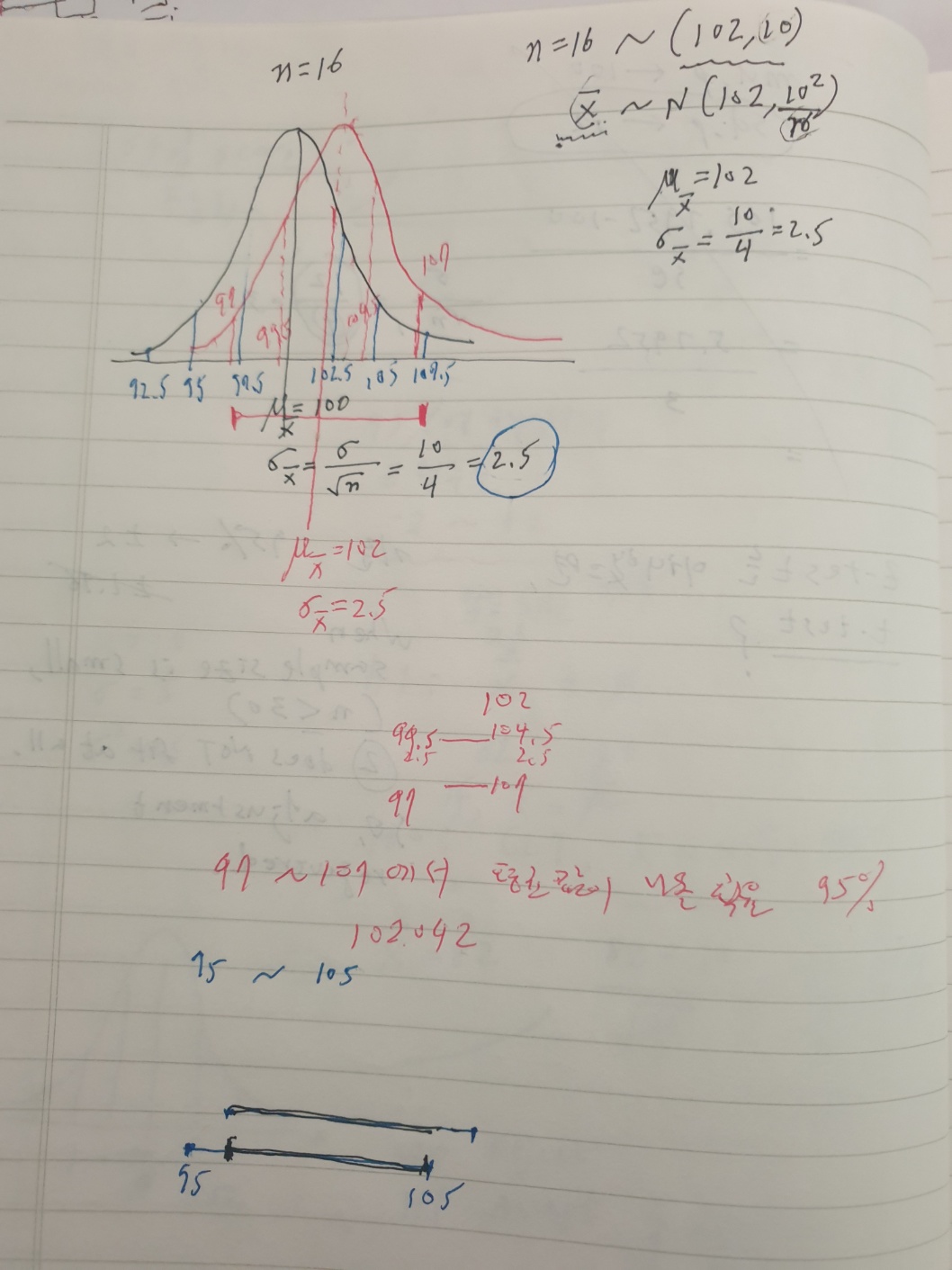
mu.pop <- 100
sd.pop <- 10
set.seed(101)
treated.group <- rnorm(16, 112, 10)
treated.group
m.tg <- mean(treated.group)
m.tg
# H1: m.tg =\ mu.pop (100) ?
# H0: if m.tg =\ mu.pop (100)
# then
# n=16 Xbar ~ N(mu.pop, 25/4)
# 즉 Xbar집합의 분산은 6.25
# 표준편차는 (표준오차, se) 2.5
# 따라서 Xbar 집합의 평균을 중심으로한
# 95% 범위는 pop.mu +- 2*(se)
# 즉, 100중 95는 95 ~ 105 사이에서 샘플의 평균이 나와야 함
# 즉, m.tg는 위의 범위에서 나와야 함. 그러나
# 나머지 5%는 95 밑이나 105 위에서 나올 수도 있음
# 그런데, m.tg = 113.0706
# 이를 근거로 영가설을 부정하고
# 검증하고자 하는 연구가설을 채택함
# 즉, treated group 과 모집단의 평균은 다르다. 혹은
# treated group은 모집단에서 추출될 수 있는 샘플이 아니라
# 다른 모집단에 속한 샘플이다 (95% 확신, 5% 에러마진)
se <- sqrt((sd.pop^2)/16)
qnorm(0.975,mean=100,sd=se)
# [1] 104.8999
qnorm(0.025,mean=100,sd=se)
# [1] 95.10009
# 그렇다면 mu.tg 값이 나올 확률은 몇일까?
pnorm(mu.tg, mean=100, sd=se)
# [1] 0.9999999
sscore <- (m.tg-mu.pop)/se
sscore
# [1] 5.22823
1-pnorm(sscore,0,1)
# [1] 8.557037e-08
a <- 1-pnorm(sscore,0,1)
b <- pnorm(-sscore,0,1)
a
# [1] 8.557037e-08
b
# [1] 8.557037e-08
a+b
# [1] 1.711407e-07
# install.packages("BSDA")
# library(BSDA)
z.test(treated.group, mu=mu.pop, sigma.x=sd.pop)
mu.pop <- 100
sd.pop <- 10
set.seed(100)
treated.group.2 <- rnorm(16, 102, 10)
treated.group.2
m.treated.group.2 <- mean(treated.group.2)
m.treated.group.2
# install.packages("BSDA")
# library(BSDA)
z.test(treated.group.2, mu=mu.pop, sigma.x=sd.pop)
set.seed(100)
treated.group.2 <- rnorm(1600, 102, 10)
treated.group.2
m.treated.group.2 <- mean(treated.group.2)
m.treated.group.2
# install.packages("BSDA")
# library(BSDA)
z.test(treated.group.2, mu=mu.pop, sigma.x=sd.pop)
> z.test(treated.group, mu=mu.pop, sigma.x=sd.pop) One-sample z-Test data: treated.group z = 5.2282, p-value = 1.711e-07 alternative hypothesis: true mean is not equal to 100 95 percent confidence interval: 108.1707 117.9705 sample estimates: mean of x 113.0706 > # 위에서 . . . . z 값이 +_2 밖이면 영가설을 부정하고 # 연구가설을 채택하게 된다
# 샘플 숫자가 작을 경우 위의 +-2 점수가 정확하지 # 않기 때문에 보정을 해주게 된다. 이 보정된 값은 # 샘플의 숫자에 따라서 (degrees of freedom) 달 # 라지게 된다
Week06
Concepts and ideas
이번 주 동영상
- https://youtu.be/hX0mbKm6M4s : z-test (z 테스트)
- https://youtu.be/06xTY1cVtb8 : z score (표준점수)
- https://youtu.be/aG8X6EUu7xI : probability in R (R에서의 확률분포함수들)
또한 R에서 데이터를 (테이블 혹은 어레이) 이용하여 function을 적용하는 것에 대해서 잘 익혀두시기 바랍니다. 이는 R cookbook의 아래 내용에 해당이 됩니다 (특히 sapply, tapply, by 등)
- Introduction
- Splitting a Vector into Groups
- Applying a Function to Each List Element
- Applying a Function to Every Row
- Applying a Function to Every Column
- Applying a Function to Groups of Data
- Applying a Function to Groups of Rows
- Applying a Function to Parallel Vectors or Lists
Strings and Dates
# pnorm # qnorm # pt # qt percentage <- .975 df <- 99 t.critical <- qt(percentage, df) # sample size = df + 1 일 때, 95%에 해당하는 점수는? t.critical t.calculated <- 3.6 df <- 8 pt(t.calculated, df)
Announcement
Assignment
Week07
Concepts and ideas
- r 에서 qnorm(proportion) pnorm(z-score) function 이해 필요
- z_score 참조
7주차 동영상
- t-test
- https://youtu.be/Eje8lR8EXPc t-test: Intro
- https://youtu.be/BL9TZbDUVWg t-test: One sample t-test
- https://youtu.be/E7QUCYRcbM0 t-test: Independent samples t-test; repeated measure t-test 일부
- https://youtu.be/CV-DY9xdxtc t-test: Repeated measure t-test 계속
- 관련 문서: t-test
- r 에서, qt(proportion, df), pt(t-score, df) function 이해 필요
- probability 참조
Probability calculation in R ← Probability in R cookbook (텍스트북)
- Introduction
- Counting the Number of Combinations
- Generating Combinations
- Generating Random Numbers
- Generating Reproducible Random Numbers
- Generating a Random Sample
- Generating Random Sequences
- Randomly Permuting a Vector
- Calculating Probabilities for Discrete Distributions
- Calculating Probabilities for Continuous Distributions
- Converting Probabilities to Quantiles
- Plotting a Density Function
Assignment
- 가설 만들어 보기
- how to write hypothesis at behavioral science writing.
- One sample hypothesis Hypothesis at www.socialresearchmethods.net
8주차 퀴즈
8주차 정기시험기간 중에 2차 퀴즈
- 시간
- 09:00 ~ (A, B교시)
- 범위
- 처음부터 One-way ANOVA test with post hoc test 까지 (R square에 대한 설명포함)
- 제 9주차 내용이지만 수업시간에 다룬 것만 시험에 나옵니다.
- 동영상은 7주차까지 보셔야 합니다
Week08
시험기간
Week09
Concepts and ideas
영상 ANOVA
- https://youtu.be/bNK5iIjAoHI : Intro to ANOVA (F-test)
- https://youtu.be/L9ns0vuvWJ8 : principles of ANOVA
- https://youtu.be/xOixsz4Qkz0 : ANOVA, calculation based on the priciple
- https://youtu.be/kyVXFS3jts4 : post-hoc test / t-test vs. ANOVA
위키페이지 참조
- Introduction
- Summarizing Your Data
- Calculating Relative Frequencies
- Tabulating Factors and Creating Contingency Tables
- Testing Categorical Variables for Independence
- Calculating Quantiles (and Quartiles) of a Dataset
- Inverting a Quantile
- Converting Data to Z-Scores
- Testing the Mean of a Sample (t Test)
- Forming a Confidence Interval for a Mean
- Forming a Confidence Interval for a Median
- Testing a Sample Proportion
- Forming a Confidence Interval for a Proportion
- Testing for Normality
- Testing for Runs
- Comparing the Means of Two Samples
- Comparing the Locations of Two Samples Nonparametrically
- Testing a Correlation for Significance
- Testing Groups for Equal Proportions
- Performing Pairwise Comparisons Between Group Means
- Testing Two Samples for the Same Distribution
vene . . . go or come
intervene
- intervenient
convene
- convention
- convent
- convenient
contravene
prevent
advent
circumvent
Assignment
Week10
Concepts and ideas
10주차 동영상입니다.
- https://youtu.be/IpuyWhk1R9g : Factorial ANOVA
- https://youtu.be/UuJhej1eJJI : Factorial ANOVA by hand
- https://youtu.be/rl6zs1lK0BE : Factorial ANOVA egs.
see w10.lecture.note
Assignment
Week11
Concepts and ideas
동영상 (총 5 개)
- https://youtu.be/vwxdhllHM-8 : Repeated Measures ANOVA, Intro
- https://youtu.be/L_jzB650Llo : Repeated Measures ANOVA in R
—-
- https://youtu.be/Cj7mxGBrIU8 : Correlations 01
- https://youtu.be/oYKFeuAn140 : Correlations 02
- https://youtu.be/aHdb4j3ybX8 : Spearman (Rank ordered) Correlation
regression
multiple regression
using dummy variables
getting started
basics
navigating in r
input output in r
data structures
data transformations
- Introduction
- Creating a Scatter Plot
- Adding a Title and Labels
- Adding a Grid
- Creating a Scatter Plot of Multiple Groups
- Adding a Legend
- Plotting the Regression Line of a Scatter Plot
- Plotting All Variables Against All Other Variables
- Creating One Scatter Plot for Each Factor Level
- Creating a Bar Chart
- Adding Confidence Intervals to a Bar Chart
- Coloring a Bar Chart
- Plotting a Line from x and y Points
- Changing the Type, Width, or Color of a Line
- Plotting Multiple Datasets
- Adding Vertical or Horizontal Lines
- Creating a Box Plot
- Creating One Box Plot for Each Factor Level
- Creating a Histogram
- Adding a Density Estimate to a Histogram
- Creating a Discrete Histogram
- Creating a Normal Quantile-Quantile (Q-Q) Plot
- Creating Other Quantile-Quantile Plots
- Plotting a Variable in Multiple Colors
- Graphing a Function
- Pausing Between Plots
- Displaying Several Figures on One Page
- Opening Additional Graphics Windows
- Writing Your Plot to a File
- Changing Graphical Parameters
Assignment
과제명: ms23.w11.ga.covariance.exercise
제출파일명: ms23.w11.ga.covariance.exercise.group##.odc (docx)
과제내용:
아래 데이터를 다운로드 받아서 두 변인 간의 상관관계계수를 구하시오.
income.happiness.csv
income.happiness.cat.csv
데이터는 수입과 행복을 측정한 것입니다. 실제 데이터를 살펴보고 R로 읽어 온 후에 R을 이용하여 아래를 구하시오. R에서의 명령어와 아웃풋을 카피/패이스트 하여 제출하시오 (fixed-font를 사용하여).
- 각 변인의 deviation score 값을 구하여 ds.inc 와 ds.hap 에 저장하시오.
- 두 변인의 SP값을 (Sum of Product) 구하여 sp.dat 에 저장하시오.
- 두 변인의 df값을 구하여 df.dat 에 저장하시오.
- 두 변인간 covariance값을 r의 cov 명령어를 이용하여 구하여 cov.dat값에 저장하시오.
- sp.dat / df.dat 값을 구하여 cov.cal 값에 저장하시오.
- cov.cal 과 cov.dat 값이 같은지 비교하시오. (힌트:
==연산자를 이용하여 확인하시오) - 각 변인의 standard deviation 값을 구하여 sd.inc, sd.hap에 저장하시오
- 우리가 배운 correlation값을 구하는 공식에 따라서 r 값을 구해서 r.cal 에 저장하시오.
- R의 cor 명령어를 이용하여 correlation coefficient값을 구하여 r.dat 에 저장하시오.
- r.cal 과 r.dat 을 비교하시오.
Week12
May 22 (월), 24 (수)
Announcement
Concepts and ideas
regression lecture note for r
동영상 Regression
- https://youtu.be/68gho4ubOjs : Regression 1. Intro
- https://youtu.be/qXSRgSh1rw0 : Regression 2. e.g. 1
- https://youtu.be/I8wt2W7-Iio : Regression 3. e.g. 2
Assignment
Week13
May 27 (월) 세번째 퀴즈
퀴즈 범위는
처음부터 regression까지
퀴즈 범위는
stats part
- 어떤 테스트를 어떤 상황아래에서 하는지에 대한 이해.
- 가령 t-test se 구하는 방법 치이점 이해
- ANOVA를 사용할 때에 대한 이해 등등
r part
- 위의 내용과 관련한 R 아웃풋 해석에 중점
Concepts and ideas
영상
- https://youtu.be/LOEinkXaskA : Multiple Regression 01 Intro.
- https://youtu.be/v6LswXPvEWY : Multiple Regression 03 Interpreting ivs
- https://youtu.be/tc6wb7fBmiY : Week13 Multiple Regression 02 Dummy variables
Assignment
Week14
June 5(월), 7(수)
영상보기
* https://youtu.be/AXMtT5cYpZ4 Factor Analysis
Concepts and ideas
Including Dummy variables
dummy variable with R
interaction effects in regression analysis
sequential regression
beta coefficients
mediation analysis
Assignment
Week15
June 12, 14
Assignment
그룹 assignment: ms.23.ga.w15.multiple.regression.groupID
그룹의 아래의 두 개 중 하나를 택하여 수행하시오. 6월 19일까지 완성 (ABB)
- 일
- data: elemapi2.csv
- available at http://commres.net/wiki/_media/r/elemapi2.csv
- api00 을 종속변인으로 하고 관련이 있을 것 같고 흥미로운 변인들을 독립변인으로 하여 (최소한 3개 이상, 그 중 하나는 종류변인이어야 합니다) multiple regression을 디자인 하고 이를 수행한 후 경과와 결과를 보고하시오
- api00을 종속변인으로 하고 두 개의 독립변인으로 avg_ed와 mealcat 두 개를 골라서 interaction을 포함한 regression을 수행한 후 경과와 결과를 보고하시오.
- 이
- data: College (in ISLR package in R)
- data에 대한 정보
library(ISLR)후?College
- 종속변인 하나를 골라서 다른 독립변인들을(최소 3개 이상) 가지고 Regression을 수행한 후 경과와 결과를 보고하시오.
- 위에서의 종속변인과 두개의 독립변인을 골라서 (숫자+숫자 혹은 숫자+종류) interaction 효과를 포함하는 Regression을 한 후에 경과와 결과를 보고하시오
Week16
June 19, 21 (퀴즈일자에만 퀴즈를 보고 수업은 없음)
Final-term
- 마지막 퀴즈
- 범위는 다음과 같습니다.
- Statistics
- R 관련 문제는 아웃풋을 이해하는지에 치중을 하시면 됩니다. 실제 명령어 사용 등에 대한 문제는 나오지 않습니다.